Create a Repository
15 min. | Beginner
Create Repository on GitHub
A GitHub repository (or “repo” for short) is an online workspace that stores your project files, tracks their version history, and enables collaboration with others. In the GW Data Science program, you will create repositories to:
- ✅ Store programming files related to your courses, including class notes, homework, assignments, and final projects.
- ✅ Collaborate with peers on assignments or final projects.
- ✅ Track changes and maintain version history for all your code and project files.
If you haven’t created a GitHub account yet, visit our Data Science Setup.
Cloning a Repository
Once the “repo” is created on GitHub, you’ll want to “clone” it. Cloning means downloading a copy of the repo to your local machine, allowing you to work on it using code editors and other development tools.
Explore, learn from, and even contribute to other people’s projects, that’s the power of an open source community!
Open Terminal (Mac) or Command Line (Windows)
Locate your GitHub folder
cd path-to-your-github-folderCopy the HTTPS of your repository from GitHub (e.g.,
https://github.com/username/my-python-project.git)git clonethe Repository:git clone https://github.com/username/my-python-project.git
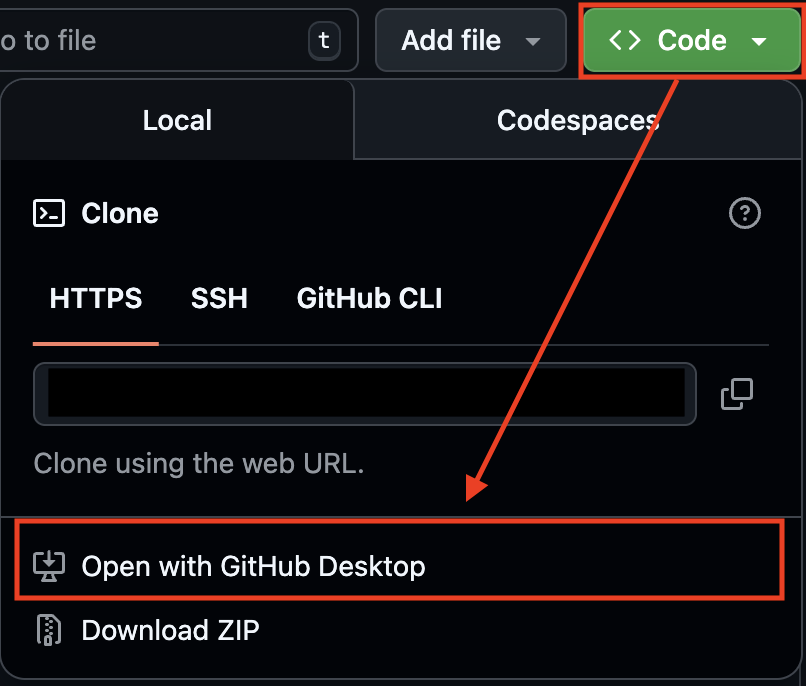
Open Your Repository on GitHub
Code → Open with GitHub Desktop
This will launch the app and prompt you to choose a local folder to clone the repository into.