Optimization
Optimization Steps
Optimization involves finding the maximum or minimum value of a function over a given domain.
There are two types of extrema:
- Global (absolute) extrema: the highest or lowest value over the entire domain.
- Local (relative) extrema: the highest or lowest value in a small neighborhood.
Steps:
Take the derivative:
f'(x)Find critical points:
Solve f'(x) = 0 and check where f'(x) is undefined.Classify using a test:
- First Derivative Test (sign change in f'(x))
- Second Derivative Test:
- If f''(x) > 0, local minimum
- If f''(x) < 0, local maximum
Evaluate endpoints (if on a closed interval) to find global extrema.
First Derivative Test
Check the sign of f'(x) around critical points:
| Behavior of f'(x) | Type of Point |
|---|---|
| Changes + \to - | Local maximum |
| Changes - \to + | Local minimum |
| No sign change | Not an extremum |
Second Derivative Test
Use the second derivative at a critical point:
f''(x)
| f''(x) Value | Conclusion |
|---|---|
| > 0 | Local minimum |
| < 0 | Local maximum |
| = 0 | Inconclusive |
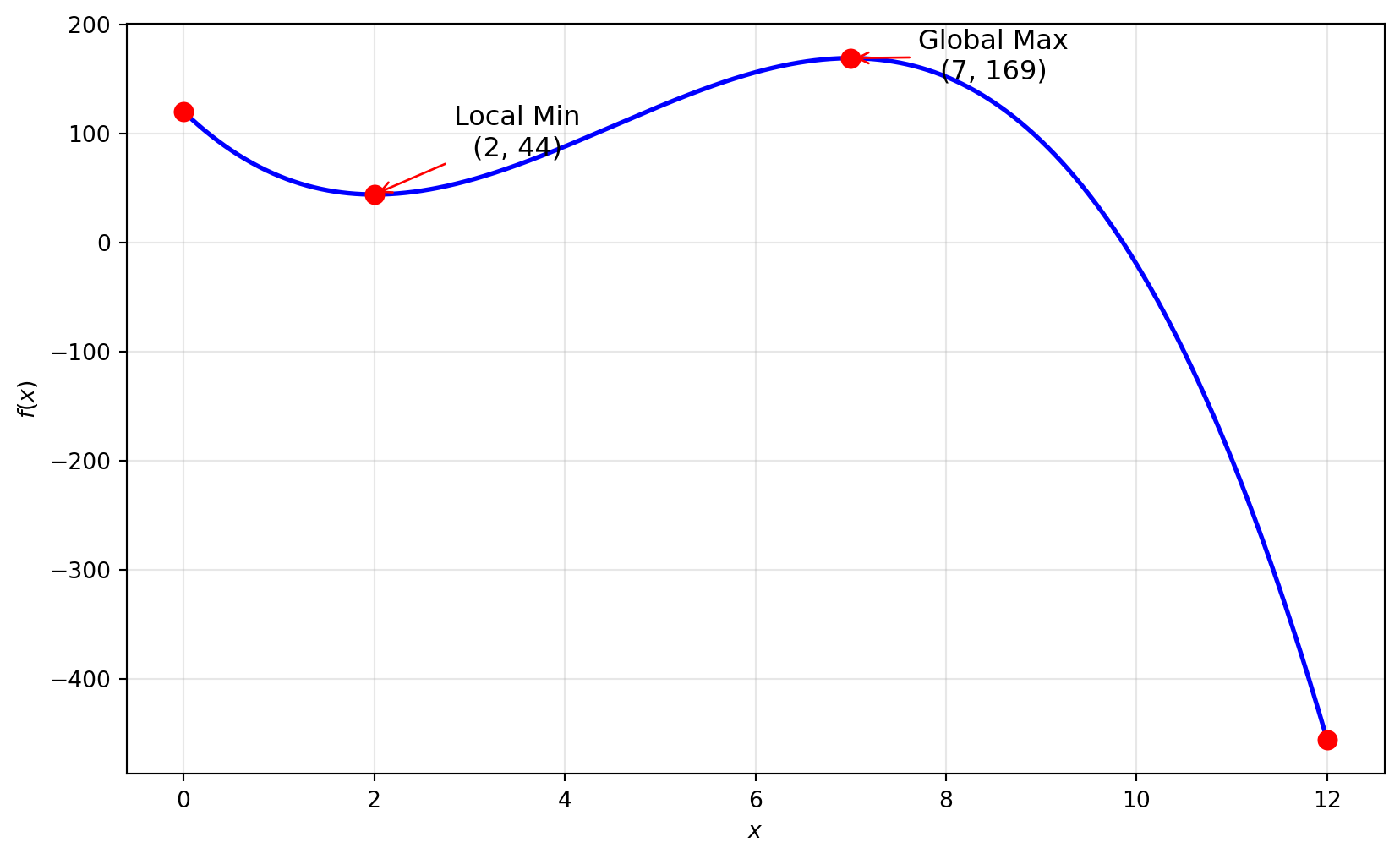
Consider the function on the interval [0,12]:
f(x)=−2x^3+27x^2−84x+120
- Take the derivative:
f'(x)=−6x^2+54x−84
- Find critical points:
Set f'(x) = 0
\begin{aligned} −6x^2+54x−84 &= 0 \\ x^2-9x+14 &=0 \ \text{(divide by -6)} \\ (x-2)(x-7) &=0 \end{aligned}
Critical points are x=2 and x=7.
- Classify using a test:
f''(x)=−12x+54
At x = 2:f''(2)=−12(2)+54=30>0 Local minimum at x = 2
At x = 7:f''(7)=−12(7)+54=−30<0 Local maximum at x = 7
- Evaluate endpoints
f(0) = 120 f(2) = -2(8) + 27(4) - 84(2) + 120 = -16 + 108 - 168 + 120 = 44 f(7) = -2(343) + 27(49) - 84(7) + 120 = -686 + 1323 - 588 + 120 = 169 f(12) = -2(1728) + 27(144) - 84(12) + 120 = -3456 + 3888 - 1008 + 120 = -456