1.1 Why Should I Learn Reinforcement Learning?
Advances in Artificial Intelligence
June 2018: OpenAI introduces the Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT), laying the foundation for subsequent LLMs.
February 2019: OpenAI releases GPT-2, demonstrating significant improvements in text generation capabilities.
June 2020: GPT-3 is unveiled, featuring 175 billion parameters and showcasing advanced language understanding and generation.
January 2021: OpenAI announces DALL-E, a model capable of generating images from textual descriptions.
April 2022: DALL-E 2 is introduced, offering enhanced image resolution and greater realism in generated images.
November 2022: OpenAI releases ChatGPT, a conversational AI based on the GPT-3.5 architecture, enabling more interactive and contextually relevant dialogues.

In essence, the AI model’s behavior closely mirrors human-like actions. This is expected, given its training on extensive datasets derived from human behavior. However, continued training on the same datasets will likely result in models that perform at a human-equivalent level. To achieve significant breakthroughs, we must explore learning methods that transcend typical human capabilities.
The Goal of Reinforcement Learning
Ultimately, as scientists, we want to discover new solutions for a task so that when an agent, or decision-maker, is placed in a novel situation it can respond intelligently (Levine 2019).
Reinforcement Learning is concerned with seeking emergent behavior, or behavior that goes beyond what people might do or think of.
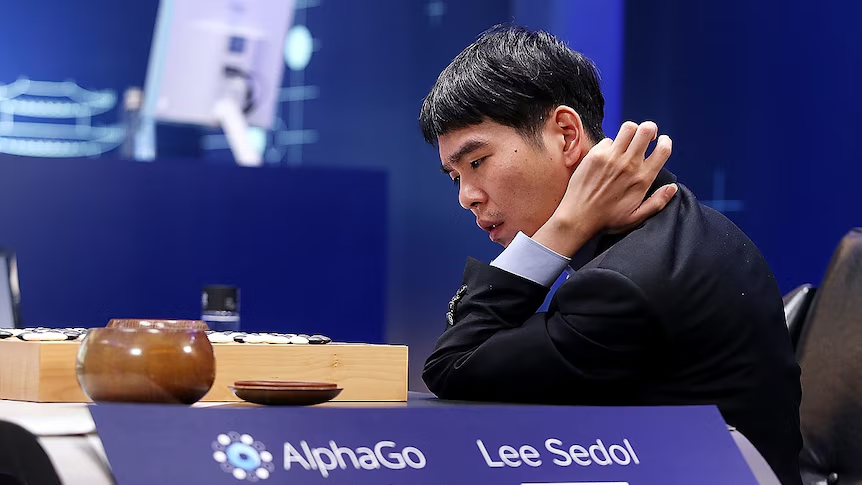
Example: AlphaGO
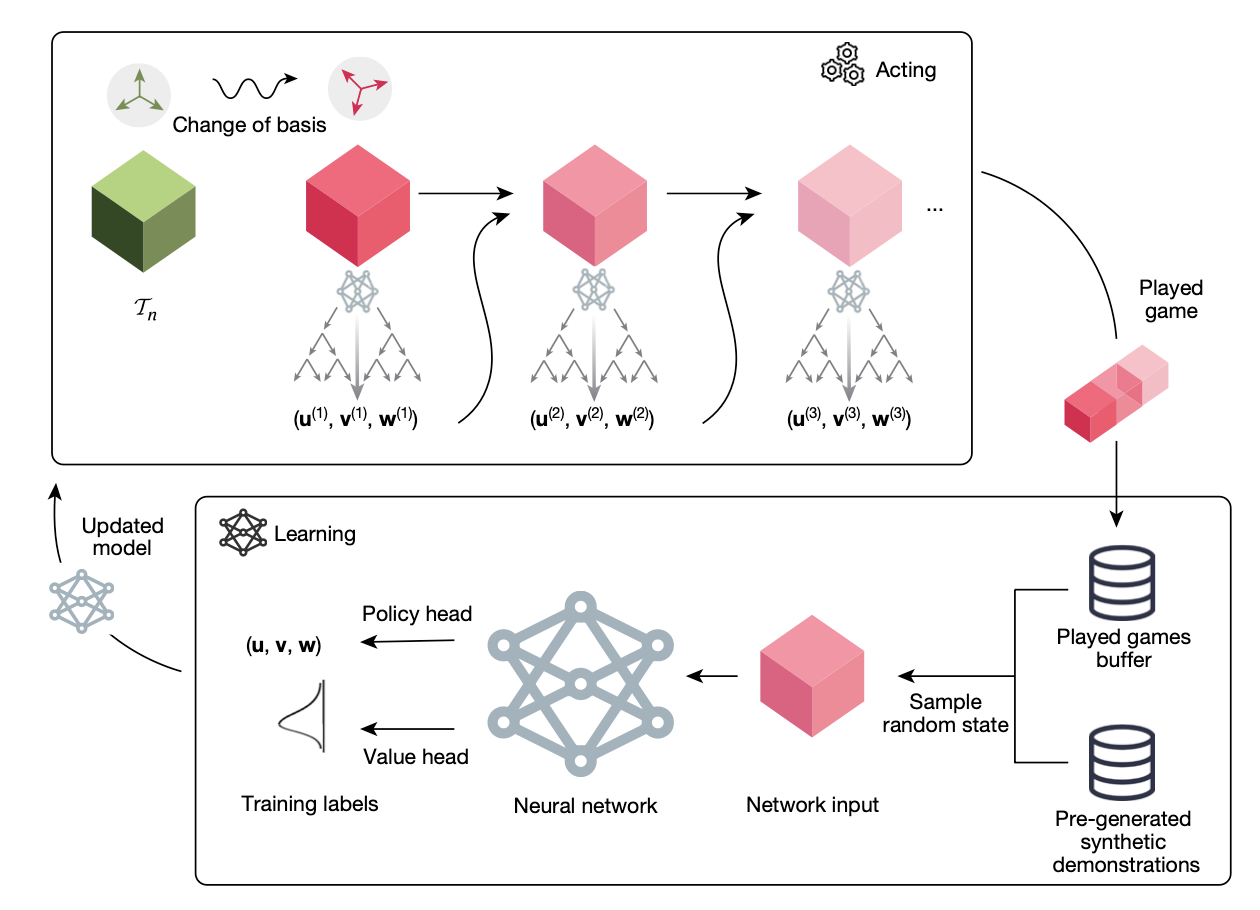
Example: Matrix Multiplication (Fawzi et al. 2022)
“Trained from scratch, AlphaTensor discovers matrix multiplication algorithms that are more efficient than existing human and computer-designed algorithms.” - Discovering faster matrix multiplication algorithms with reinforcement learning